Anti-abortion researchers ‘exaggerate’ and ‘obfuscate’ in their scientific papers – but by the time they’re published, it’s too late
A pharmacy professor who strenuously avoids heated political discussions is an unlikely candidate to get involved in a fight over abortion, particularly one as high stakes as a case now before the supreme court: the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) v. the Alliance for Hippocratic Medicine (AHM).
But when the professor Chris Adkins of South University in Georgia emailed his concerns about an academic article to the editors of Health Services Research and Managerial Epidemiology, that’s exactly what happened.
The article had been published by an anti-abortion research institute and, perhaps unsurprisingly, concluded that medication abortion was far less safe than the accepted scientific consensus – one established by more than 100 peer-reviewed studies across multiple continents and two decades of real-world use.
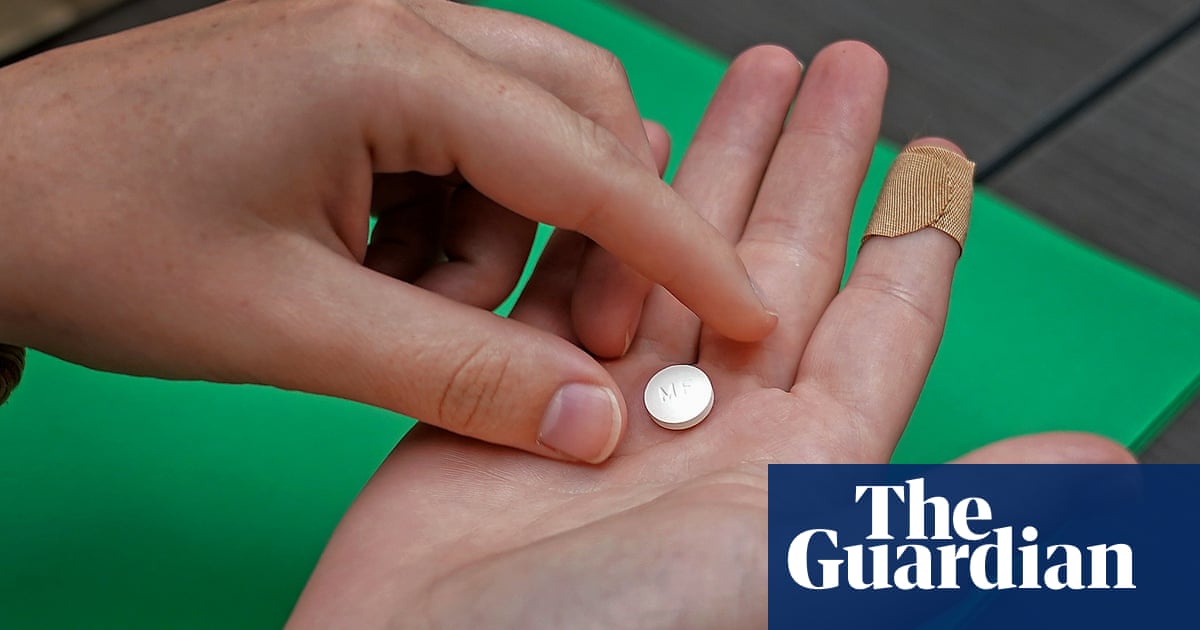
“The way this study used this situation to exaggerate, and I’ll say obfuscate, the truth behind mifepristone’s safety profile is where I thought: ‘I’ll reach out to the journal and say I’ve got these issues,’” said Adkins, referring to the drug targeted by researchers. Mifepristone is one half of a two-pill regimen that treats miscarriage and ends early pregnancy, and its future hangs in the balance of the supreme court case, to be heard this week.
“I honestly didn’t think I would be the first to do that,” said Adkins.
Within a couple days of Adkins’ complaint, the global academic publisher Sage, which publishes the journal, began investigating. Within weeks, Sage retracted not one but three papers by the anti-abortion researchers.
Adkins’ concerns go to the heart of a problem that has bedeviled scientists for at least a decade: the judicial system’s repeated adoption of poor-quality evidence to justify litigation and legislation to restrict abortion. Often that evidence is produced by the anti-abortion movement itself.

anti choice / forced birthers are utterly deranged